
Table of Contents
Introduction
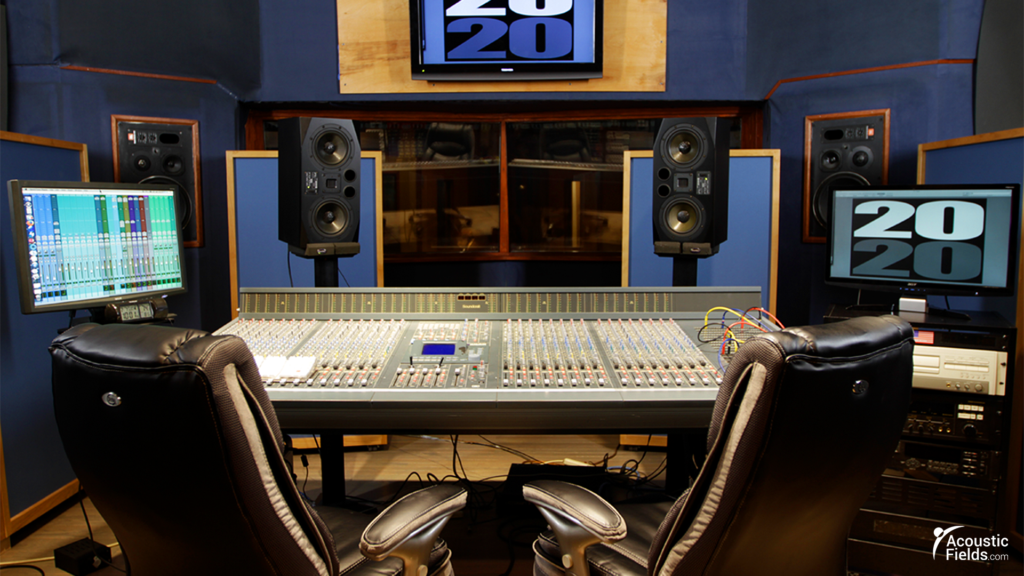
A mixing room is defined as a room where you mix music. Let’s step back and examine the mixing room process so we can really understand the mixing room process and function. A mixing room takes raw recorded tracks of music and voice and combines them together in a way that is musical and has speech intelligibility. The live room is where the music and voice are recorded within. The mixing room is where all of those performances and recordings get sent for processing.
A mixing room engineer is a person of many talents. They must have the ability to hear everything in the original recording. Once that feat is accomplished, by having good rooms to work within, the music and voice recordings are processed to improve resolution and reduce noise levels. The first few steps are to hear everything then to reduce the noise floor in the recordings to the lowest levels. No noise must be the goal.

Music Mixing: Creative Blending by Engineers
Once the mixing room engineer has the above issues addressed, they can then begin the blending process. Blending the existing music and voice recordings with two processes. The first is to get the tracks assembled so that they make some type of musical sense. The second step is to add many processing signals to add or subtract from the original recordings.
This is where the creativity of the engineer is critical and oftentimes the only reason the engineer was hired in the first place. It is the creativity skill set using the digital processing tools of which there are literally thousands. What signal processing to use where in the recording can not be an easy task. it must rely upon many years of experience along with a technical knowledge of what the final recording will sound like. A musical recording is always a blend of musical talent and quality mixing.

Noise Control: Building Effective Studio Barriers
One of the most critical variables to manage in any critical listening environment such as a mixing room is noise transmission. Noise transmission is defined as sound energy from a source, let’s say garbage truck, leaving the garbage truck and then getting into our mixing room where the noise floor must remain low so the engineer can hear everything that is in the raw recorded mixes. In order to keep noise inside the studio and from getting into the studio, you build a barrier.
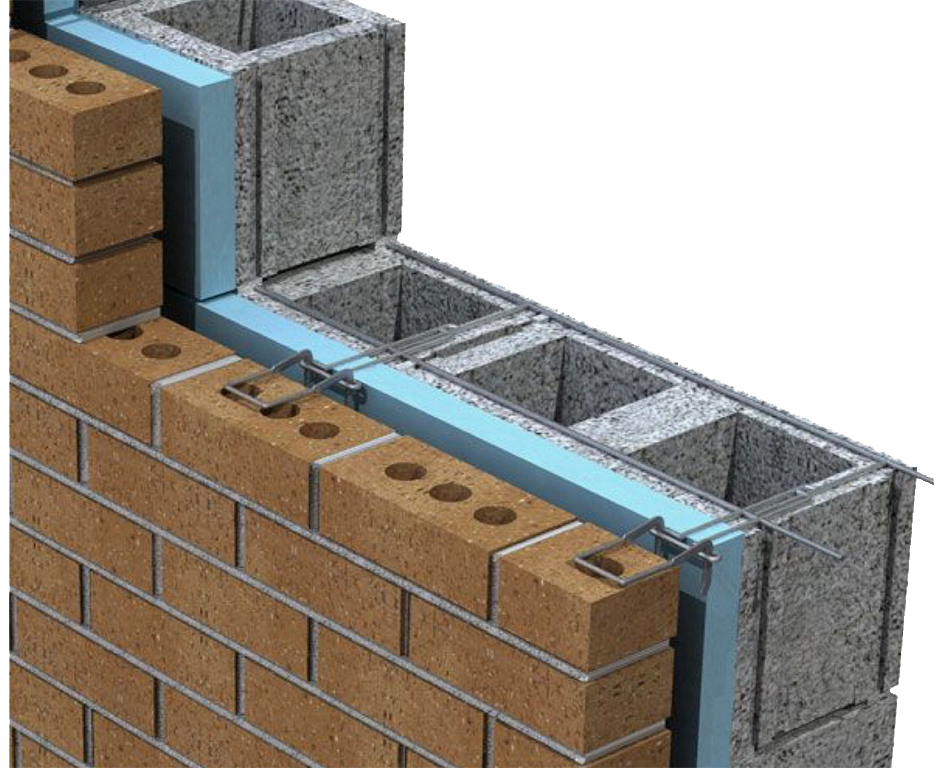
A barrier is a scientific designed structure that is the result of materials and design of the noise that is trying to get into the studio from outside and then the flip side of that which is noise from inside the studio getting out and escaping to adjacent structures. All noise inside and outside of the studio must always be measured for both frequency and amplitude. The frequency is where the noise lives on the human hearing range. The amplitude is how strong the noise is at that frequency.
Custom Barrier Design: Accurate Noise Measurement
At Acoustic Fields, we have a process to assist you with measuring noise issues. We have apps that we send you to download on your phone. You then take the noise measurements twice a day using our apps and your phone. You take two measurements a day. You take one during the quietest part of each day and another at the loudest part of each day for all outside noise issues.
The inside noise created by a mixing room can be simulated to provide frequency and amplitude numbers. Once you take the numbers with your phone, you record the measured numbers on our online data sheet and then send them to us. We analyze your noise numbers and then send you a drawing of the structure you need to build. The barrier design is specifically based on the noise numbers that you have taken.
No Guesswork for Effective Noise Control
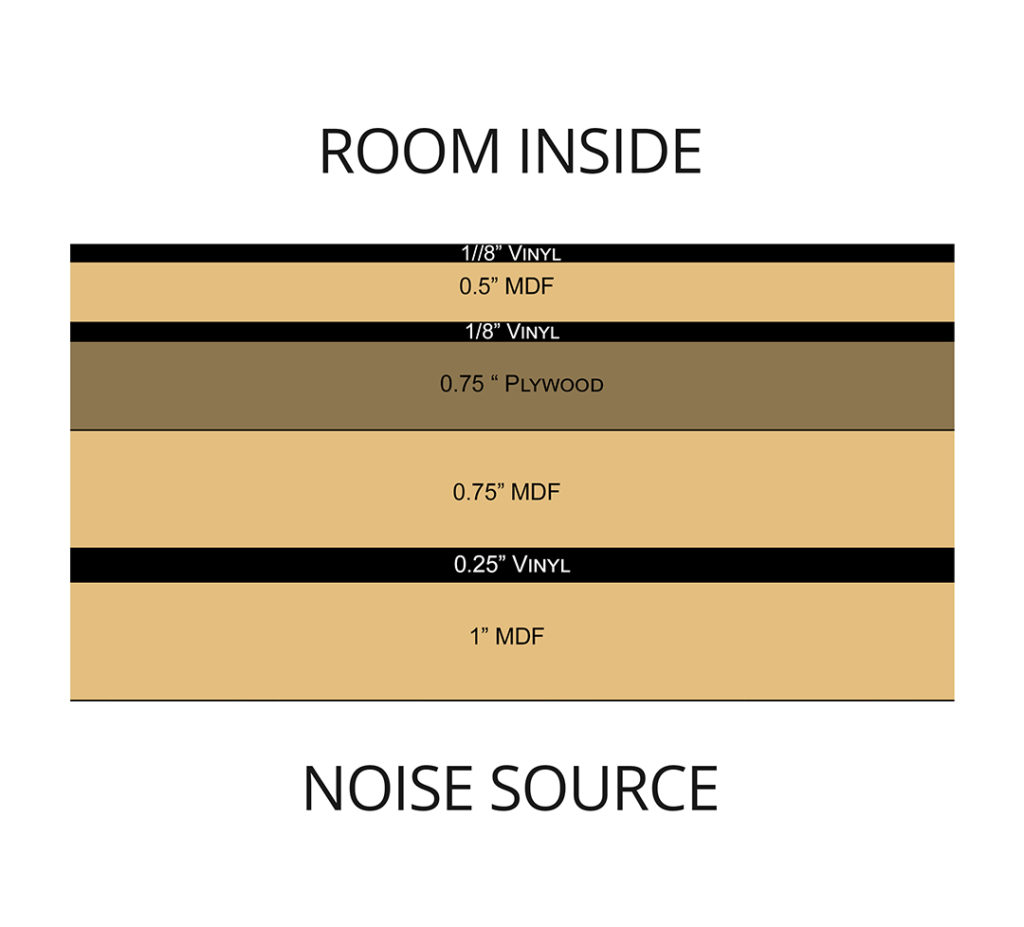
Every material type, every material thickness along with the way the chosen materials are arranged plays an important part in the effectiveness of the barrier design. There is no cutting corners or guessing with noise. Cutting corners and guessing means that the end result will not perform at all of the required noise frequencies. Noise that is below 125 hz. requires a different barrier construction type with more layers of different materials than noise above 125 hz.. Noise above 125 hz. is voice frequency range.
Energy that is noise below 125 hz. is garbage truck noise that sets off parked car motion sensor alarms. You must measure noise since guessing can be an expensive option. Most guesses we see do not work well and clients call us asking what can be done to improve upon their design and construction failures. Most of the time they have to demo it and start over. You do not want to spend one dollar more or lose one more dollar with noise transmission issues because you will never get it back. It is money that is baked into the property with no credit given in value for a quiet room.
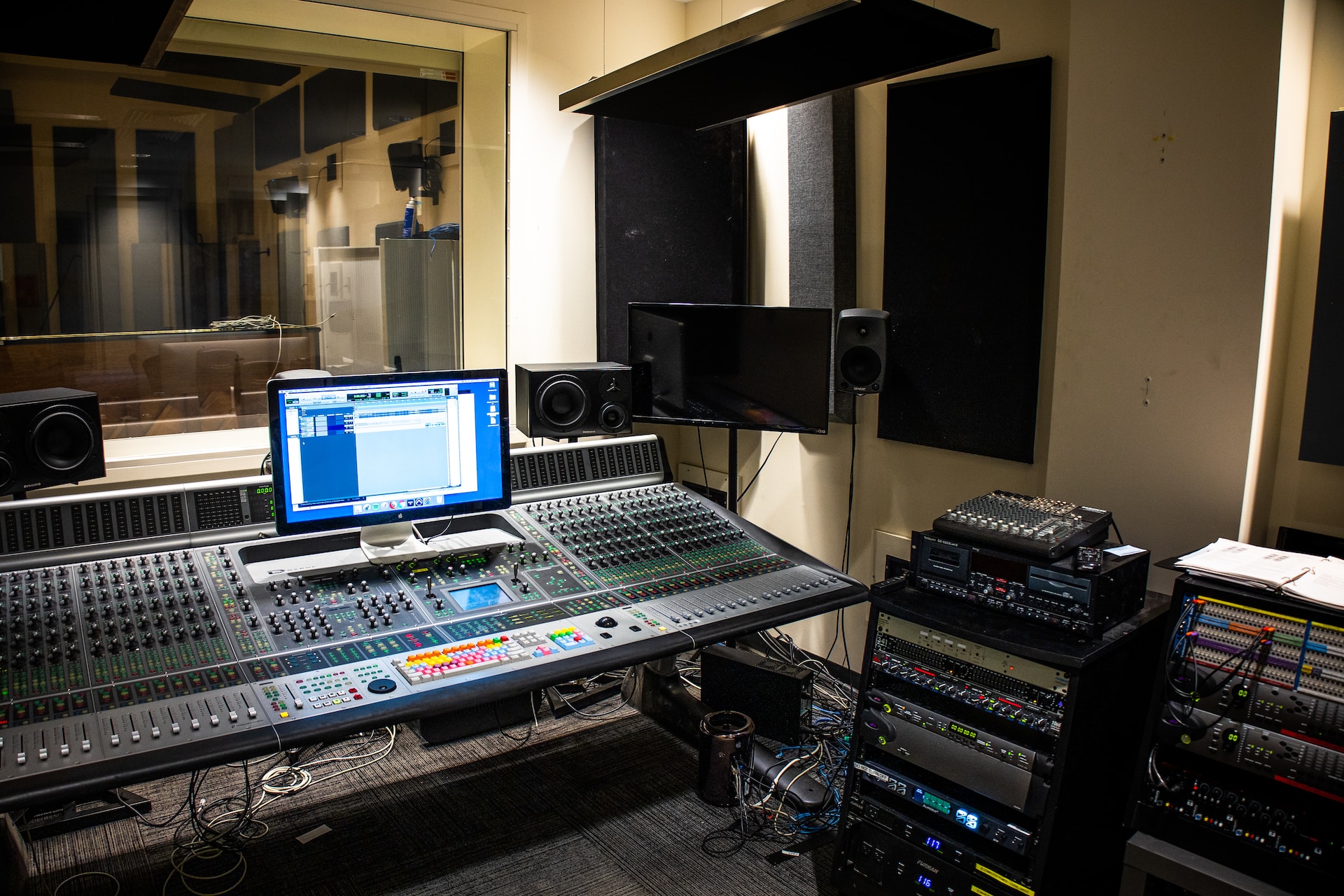
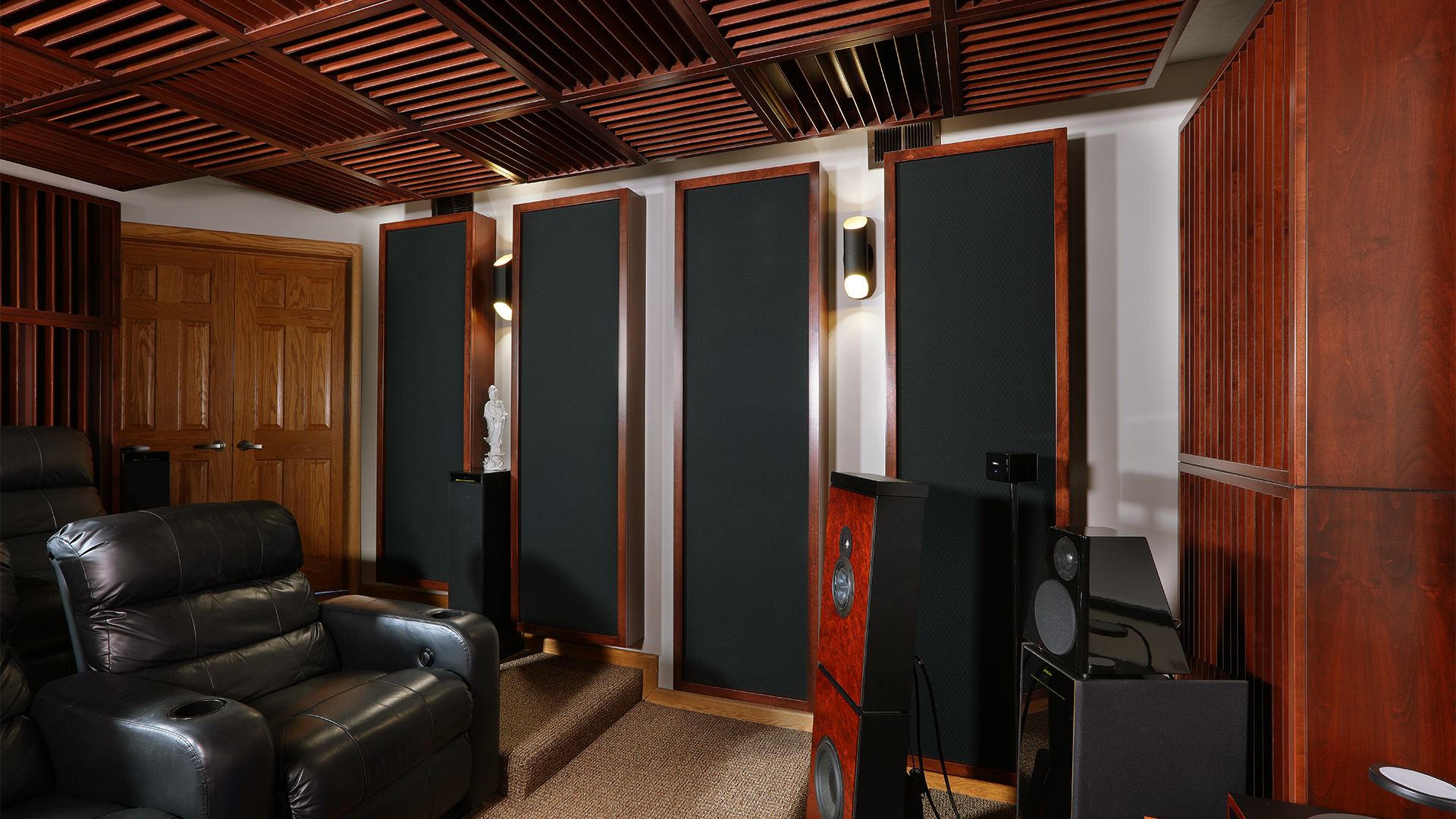








The discussion on ductwork noise transmission from Acoustic Fields highlights crucial aspects of HVAC system acoustics. The movement of air…
Great build plans. thank you Denis
You must use absorption. Never place a chair against a wall.
A friend and I built several diffusors using these plans and they turned out absolutely beautiful. Very good instructions and…